The ultimate goal of cybersecurity is to protect your organization from all possible threats. And you can only achieve this goal if you have a comprehensive vulnerability management plan. It lets you identify, assess, and eradicate areas of concern.
You have tons of applications, processes, and software. It takes work to keep up with updates and upgrades for everyone. What you can do is have a perfect vulnerability plan that helps you identify, assess, fix, and report security vulnerabilities promptly. And it is essential to understand the
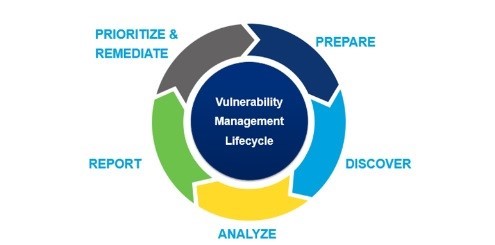
5- Steps of the Vulnerability management Cycle to strengthen your organization's cyber defense system.
Step 1: Assessment
The first part of your vulnerability management plan is to assess your data and network vulnerabilities. In this phase, security teams will identify existing security vulnerabilities- weak points which can be exploited by unauthorized personnel or threat actors. Security analysts perform regular vulnerability scans in the system to detect malicious actors' vulnerabilities or easy entry points. If you have installed an EDR on your endpoint, it will also help you identify weaknesses in your overall system.Step 2: Evaluation
Once you identify a vulnerability, the next important step is the evaluation of every vulnerability. You must analyze them and highlight their impacts, such as reputational damage or financial losses.
It's time to prioritize all those vulnerabilities that pose the greatest threat to your business's security. When you have vulnerability assessment tools, generally, they score vulnerability based on their risks and impact.
A critical vulnerability needs an immediate response.
Low-level vulnerability is the one that can't be exploited by criminals easily or whose impact is minimal.
You won't need a separate vulnerability assessment tool when you have a powerful Endpoint Detection and Response Solution such as Xcitium EDR because this EDR has a built-in Vulnerability management tool, which scores all vulnerabilities and also issues their patches.
Step 3: Act
Once you identify and evaluate vulnerabilities, the next step would be to act. Different exposures require different remediation. For example, you can patch existing software or hardware system.
When vulnerability is critical, expert vulnerability managers usually implement additional security protocols and measures. If there is an outdated application, you can update it readily. The purpose of acting upon risks is to reduce and mitigate this vulnerability.
Step 4: Reassessment
According to Positive Technologies Study, 84% of companies have high-risk vulnerabilities in their external networks. Any organization can deal with half of these vulnerabilities with regular updates of software and applications.
Many organizations perform penetration testing after patching their vulnerabilities, so they can understand whether their network is still at risk or not. Reassessment is an essential step in vulnerability management. It lets you identify new threats that require immediate action. Period reassessment is vital to safeguard your overall IT Posture.
Step 5: Reporting and Improvement
The last step of the vulnerability management plan is to get the complete report and start improving applications, procedures, and processes. This system improvement will help you manage Vulnerability and threats. There is a need to improve your network constantly.
Difference Between Vulnerability Assessment and Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability assessment is always performed after scanning your business network, process, apps, and endpoints. It's a process where every vulnerability is evaluated to separate the most critical vulnerability from the harmless one. Vulnerability Assessment is a part of vulnerability management, a broad term. During this process, you will assess a vulnerability and find the best way to patch and manage it.
How Does Xcitium Help Organizations with Vulnerability Management?
Remote work culture has become a trend all over the world. Your business's network is connected to multiple remote devices. Now, your overall system also becomes vulnerable if any of these devices and outdated software or some vulnerabilities in their applications or browsers.
You can only remind your employees some of the time to update their applications or software, and it's a hectic task to deal with. So, the better solution is to install Xcitium EDR- Endpoint Detection and Response. This tool provides endpoint-level security.
EDR by Xcitium will monitor all your endpoints in real-time and offer your security teams excellent visibility into overall security postures. They can check vulnerabilities in the system and get an alert as soon as threat actors try to access your system via a weak link or endpoint.
It's time to be proactive with your cybersecurity defense. Install Xcitium EDR and manage vulnerabilities throughout your IT network.
Wrap up
Every organization faces serious cyber threats every second. Nothing can offer your system and network a better security layer than a vulnerability management plan. There is a need to implement all five steps of the vulnerability management cycle and use the proactive approach of security, aka deployment of Xcitium EDR. Once you have both security approaches in place, you can rest assured that your business is ready to deal with any circumstance that may come its way!
