What’s The Difference Between EDR and DLP?
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) and Data Loss Prevention (DLP) are two essential cybersecurity solutions, each serving a unique role in protecting an organization’s digital assets. While both focus on security, they address different aspects of cyber threats and data protection.
EDR is designed to detect, investigate, and respond to cyber threats at the endpoint level. Endpoints include devices such as desktops, laptops, servers, and mobile devices that connect to a network. EDR continuously monitors these endpoints for suspicious activities, using behavioral analysis, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to identify potential threats. When a potential attack is detected, EDR provides real-time alerts and enables security teams to take immediate action. It can also automate responses to contain threats before they spread. EDR is particularly effective against malware, ransomware, and advanced persistent threats (APTs) that traditional antivirus solutions might miss.
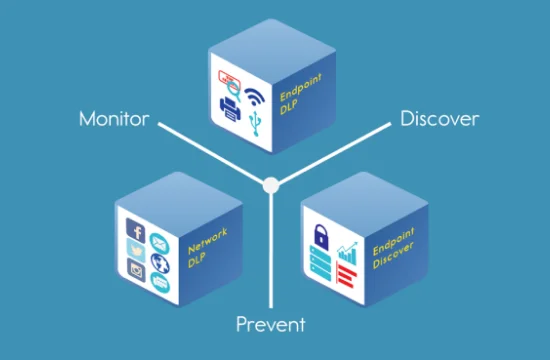
On the other hand, DLP is designed to prevent the unauthorized access, transmission, or exfiltration of sensitive data. Organizations use DLP solutions to enforce data security policies and ensure compliance with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS. DLP works by monitoring data in motion (network traffic),data at rest (stored files),and data in use (active applications and processes). It can block or restrict users from transferring sensitive information via email, USB drives, cloud services, or other channels. DLP solutions rely on content inspection, pattern matching, and policy enforcement to prevent data leaks or breaches caused by human error or insider threats.
The primary difference between EDR and DLP lies in their objectives. EDR is focused on threat detection and incident response, aiming to stop cyberattacks before they cause significant damage. It is a reactive solution that continuously analyzes endpoint activity to detect anomalies and mitigate risks. In contrast, DLP is a proactive measure that prevents data breaches by controlling how sensitive information is accessed, shared, and stored.
Another key distinction is their approach to security. EDR operates at the endpoint level, analyzing system behavior, detecting malicious activities, and providing forensic data for threat investigations. DLP, however, operates across the entire organization’s data flow, ensuring that sensitive information does not leave the network or fall into the wrong hands.
Organizations often deploy both EDR and DLP together to achieve comprehensive security. EDR protects against external cyber threats, while DLP safeguards confidential data from insider risks and accidental exposure. Together, these solutions create a layered security strategy that enhances an organization’s resilience against cyber threats and data breaches.
Comparing EDR and DLP Capabilities
When comparing Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) and Data Loss Prevention (DLP),it is important to understand how their capabilities align with an organization’s cybersecurity needs. While both solutions contribute to overall security, they focus on different aspects of protection and operate in distinct ways.
EDR is primarily designed to detect, analyze, and respond to threats targeting endpoints, such as desktops, laptops, servers, and other devices connected to a network. It continuously monitors endpoint activity, looking for anomalies that indicate potential cyber threats. EDR uses behavioral analysis, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to identify suspicious patterns, providing real-time alerts to security teams. One of its core capabilities is forensic analysis, allowing organizations to investigate security incidents and understand how a threat entered the system, how it spread, and what data may have been affected. Additionally, EDR solutions often include automated response mechanisms, such as isolating infected endpoints, stopping malicious processes, and rolling back changes caused by ransomware.
DLP, on the other hand, is focused on preventing the unauthorized access, transfer, or leakage of sensitive data. It works by monitoring and enforcing policies on how data is accessed, stored, and shared across an organization. DLP solutions inspect data in motion (network traffic),data at rest (stored files),and data in use (applications and endpoints). By using content inspection techniques such as pattern matching, keyword detection, and fingerprinting, DLP can identify sensitive information like credit card numbers, social security numbers, or intellectual property. If an unauthorized attempt to move or share this data is detected, DLP can block the action, encrypt the data, or alert administrators. This makes DLP a crucial tool for compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA.
When comparing their capabilities, EDR is more effective at stopping cyberattacks in real time, mitigating threats that could lead to data breaches, while DLP focuses on ensuring that sensitive data does not leave an organization’s controlled environment. EDR is a reactive technology that detects and responds to security incidents, whereas DLP is proactive, preventing incidents from occurring in the first place.
For organizations looking to build a robust cybersecurity framework, combining EDR and DLP can provide comprehensive protection. EDR secures endpoints from cyber threats, while DLP ensures that sensitive data remains protected against insider threats, accidental leaks, and compliance violations. Together, they create a multi-layered security approach that reduces both external and internal security risks.
Combining EDR and DLP for Maximum Security
Combining Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) and Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is a strategic approach to achieving maximum security in an organization’s cybersecurity framework. While EDR focuses on detecting and responding to cyber threats at the endpoint level, DLP is designed to prevent unauthorized access, transfer, or exposure of sensitive data. By integrating both solutions, organizations can create a multi-layered security strategy that effectively mitigates both external and internal risks.
EDR plays a crucial role in protecting endpoints from cyber threats such as malware, ransomware, and advanced persistent threats (APTs). It continuously monitors devices for suspicious activity, using behavioral analytics and artificial intelligence to detect anomalies. When a threat is identified, EDR provides real-time alerts, allowing security teams to investigate and respond promptly. Some EDR solutions also offer automated remediation, such as isolating infected devices, stopping malicious processes, and restoring compromised files. This level of threat detection and response is critical in today’s evolving cyber threat landscape.
DLP, on the other hand, ensures that sensitive data remains protected by monitoring and controlling how it is accessed, used, and shared. It enforces policies that prevent unauthorized users from sending or storing confidential information outside approved environments. DLP solutions inspect data in motion (network traffic),data at rest (stored files),and data in use (applications and endpoints) to prevent breaches caused by insider threats, accidental leaks, or compliance violations. By preventing the unauthorized transmission of sensitive data, DLP reduces the risk of financial loss, regulatory fines, and reputational damage.
Integrating EDR and DLP strengthens an organization’s security posture by addressing both threat detection and data protection. For example, an organization using EDR alone may detect and stop malware but could still be vulnerable to data leaks if sensitive files are improperly accessed or shared. Conversely, an organization relying only on DLP may prevent data leaks but remain exposed to endpoint-based cyberattacks. By deploying both solutions, businesses can detect and respond to threats while ensuring that critical data is not compromised.
An effective way to integrate EDR and DLP is through a centralized security strategy that includes unified monitoring, threat intelligence sharing, and automated response mechanisms. By leveraging both technologies together, organizations can quickly detect and neutralize threats while enforcing strict data security policies.
Ultimately, the combination of EDR and DLP provides a comprehensive security approach that protects against both cyber threats and data breaches. This layered defense strategy ensures that endpoints remain secure while preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information, allowing businesses to operate with greater confidence in their cybersecurity resilience.