How Ransomware Infects Systems?
Updated on October 11, 2022, by Xcitium

With the rise in ransomware attacks, it is estimated that organizations may be hit globally with a cost of $20 billion by 2021, according to Cybersecurity Ventures. Of course, ransomware attacks are increasing, and the method of attacks revolves around phishing. Through email phishing and the likes, ransomware criminals can infect victims’ systems with the malware, which results in data encryption and subsequent requests for a ransom.
Curious to know more about how does ransomware infects a system? This article covers a large part of that other related subject matter—ransomware attacks.
What Is Ransomware?
Ransomware is a type of malicious software that affects a computer user by restricting them from accessing their data. It is used by cybercriminals to extort people or organizations whose data they have hacked into, and they hold it hostage until the demanded ransom is paid.
If the ransom isn’t paid within the stipulated time put by the cybercriminals, they may leak the data to the public or damage it entirely. Ransomware is one of the major problems organizations are facing. Since the mid-2000s, when ransomware attacks became vile, businesses, individuals and government agencies have been victims, costing the huge sums to retrieve their systems.
How Does Ransomware Infect A System?
As mentioned above, phishing is one of the widely used methods. The attackers broadcast malicious content in emails, social media, ads, website pop-ups, etc. Let’s take a more detailed look at these methods.
Phishing Emails
This is one of the common methods used by cybercriminals to spread ransomware. The emails are created carefully so the victim can be tricked into clicking the link or opening an attachment in the email. The link or attachment contains the malicious file that will attack the system, and once it is clicked, it will gain access to the system files and data.
Once the malware enters a computer, it encrypts the files, and in some cases locks the owner or computer users’ outs. More advanced ransomware will spread to other systems (computers and servers) connected to the network.
Website Pop-Ups
Ransomware can also infect your system when you click malicious pop-ups on random websites. Though not all website pop-ups are harmful, cybercriminals also use this means to get their victims. Pop-ups from ransomware attackers would probably ask you to update an application on your computer or trick you that your system is infected with malware and you need to click a link to rid the malware. You should avoid such requests to prevent malware attacks.
Remote Control Desktop
Remote control desktop is created to offer IT administrators the possibility to access a system remotely for their work. Even though this was created for legitimate purposes, cybercriminals have seen it as a money-making venture.
Remote control desktop runs over port 3389. With a lot of systems having port 3389 open, cybercriminals can hack into the systems they find vulnerable to attacks. They will gain access to it by using brute-force attempts to log in as an administrator.
The moment the cyber criminals make themselves an administrator, they will have full access to the computer and encrypt all data. Some cybercriminals go further by disabling endpoint security or by deleting windows file backups.
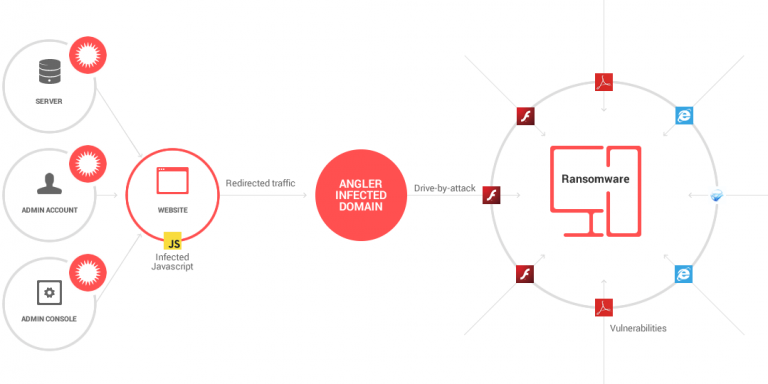
Drive-By Downloads
Attacking a user’s system through this method occurs without the user knowing—the ransomware attacks when the user visits a website that has been compromised. The user doesn’t need to click on anything before the malware spreads.
Cybercriminals usually make use of drive-by downloads on a legitimate website, especially if the website is vulnerable. However, other cybercriminals set up a website instead of hacking into one. Once a user visits a legitimate website embedded with the malware, they will be redirected to another site where the cybercriminals have full control.
Once the user’s system has been hijacked, a ransom note will appear demanding payments for the unblocking of the system and decrypting of files.
How To Prevent Ransomware
Avoid Unverified Links
This is paramount if you want to stay safe. Don’t click on emails from unrecognizable companies or emails you didn’t subscribe to. Also, avoid unfamiliar websites.
Update Your Operating System And Software Frequently
Keeping your operating system and software updated also helps in preventing you from ransomware attacks. When you update them, you will get the benefit of having the latest security patches. This makes it difficult for cybercriminals to target vulnerable software.
Use Security System
Antiviruses/antimalware programs can help block malware attacks. However, you also need advanced security systems as advanced threats can sometimes trick antiviruses. You can learn more about advanced security systems here if you’re not sure how they work.