Endpoint Security Solutions For Business
Updated on October 11, 2022, by Xcitium

We live in an age where every other day is witnessing a security attack of one kind or the other. Although these security threats are also various, all of them have one factor in common: all of them seek an associate degree entry purpose to interrupt into the network. These entry points can be at intervals or outside of the network. However, more typically than not, the attackers target those that square measure outside – remote devices like laptops, smartphones, tablets, etc., – as a result they’re a lot easier to interrupt. These entry points are called endpoints. Because they are present at the far end of the network.
Why Endpoints Are Much Preferred Targets For Hackers
Since corporate decided to relax their network policies and allowed employees to access the corporate information outside of the network using various remote devices, these devices have potentially become the ‘weakest points’ of the network. Because if these devices fall into the wrong hands (hackers), it will open up access to the entire network. Or at least to some elements within that network. Therefore these endpoints are potential ‘entry points’, which when not protected well-enough, can pave way for easy hacking.
Another reason why these endpoints are considered the weakest points within the network is because of the human factor involved. These endpoints are operated by humans and it is easier to trick them and thereby gain access to the network (example: phishing attacks) than trying to break into some other part of the network which may be machine-controlled.
So How Can You Protect Your Corporate’s Endpoints?
The answer is endpoint security software. As the name suggests, deploying this software within your network will ensure your network is secured against various endpoints of your network; at the same time, ensuring the security of the endpoints themselves. It does so by creating stringent network policies, establishing secure connections between the endpoints and your network, vetting endpoints before they gain access to the network and so on.
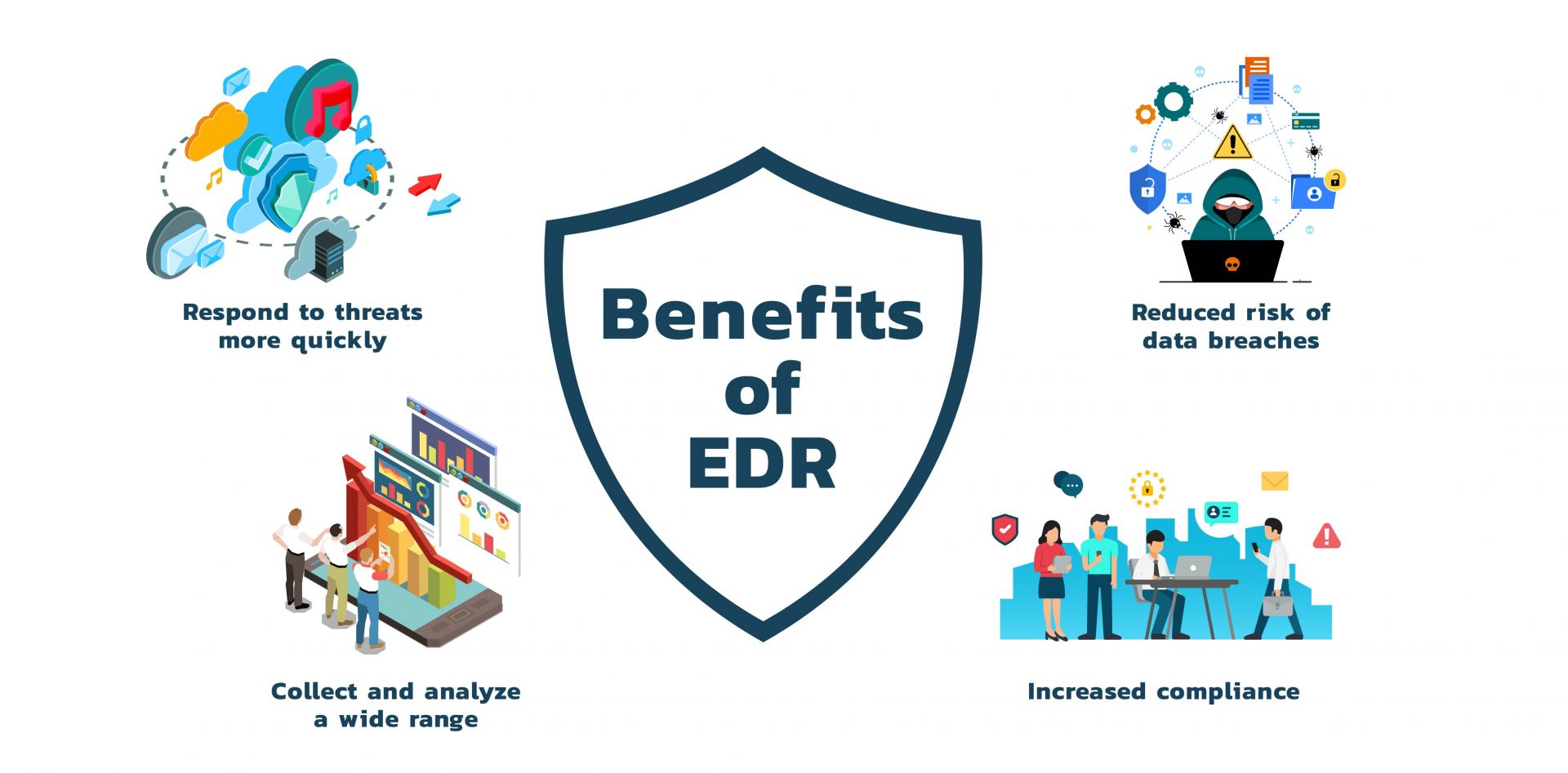
3 Significant Ways In Which Endpoint Security Software Helps E-Businesses
1. Early Detection of Security Threats
Endpoints are often the starting points of hacking. Therefore if you protect your endpoints well-enough, then the chances of hackers hacking into your network reduces greatly. And even if they do successfully break these endpoints, the constant monitoring capabilities will help businesses ensure the problem is nipped in the bud without spreading to the entire network.
2. They Reduce False Positives
Attackers often try to appear legitimate to the various security systems. To do so, they leverage endpoints and gather intelligence about the targeted organization. Learning company operations and employee behavior helps them better ingrain themselves into a system without appearing too conspicuous since they are posing as legitimate users.
Hackers also know users often commit mistakes and don’t always follow normal patterns; therefore, they sometimes replicate this employee behavior as well. Because of this reason, many security solutions produce irrelevant notifications, that do not necessarily indicate hacker activity and instead overwhelm security experts.For example, a failed login attempt may seem suspicious at first glance, but in reality might be a busy employee. Because endpoint data can expose whether there was keyboard or mouse activity at the time of the failed login, security personnel can easily decipher between a benign mistake and hacker activity.
To differentiate the real user from hackers in case of such circumstances, you need endpoint security software.
3. They Provide The Bigger Picture
Since endpoint security software is installed on every machine of your network, they’ll provide the bigger picture of your IT environment. They’ll provide enough information using which you can easily gauge the health of your network and also any suspicious activity which would otherwise go unnoticed. Therefore you can achieve great levels of network transparency – which is probably the need of the hour considering it’s raining security threats these days – using endpoint security software.